Printable Version
The Knowledge Sharing Foundation
Questions and Answers
September 16, 2003
Q-1: What is needed to support awareness of natural and cyber
events in real time?
Q-2: What is needed to support community use of analytic tools?
Q-3: What are the benefits to Industry
Q-4: What are the Foundation Elements
Q-5: Examples of Innovation
Q-6: Why are educational processes important?
Q-7: How does the software compensation model work?
Q-8: How are test sets made available to the competitive communities?
Q-1: What is needed to support awareness of natural and cyber
events in real time?
A-1: The structure of data produced from measurement.
• Real time web harvest of natural language discourse (Memetic
measurement)
• Cyber intrusion instrumentation and analysis (Cyber measurement)
• Global measurement of reports from medical professionals
(Genetic measurement)
• Measurement of social network relationships and dynamic boundaries
of social systems (as applied to mapping asymmetric threats)
A-2: New stratified theory
• With an aggregation of invariance in the structure of data.
• With a separation of statistical and categorical artifacts
in correspondence with human memory processes and human anticipatory
responses
• With the production of just in time machine-ontology formation
as cognitive enhancement
• With the development of event templates indicating meaningful
constructs
A-3: Educational processes that allow users of intelligence
system to work within the limitations of machine and artificial intelligence.
• University course credit
• Professional Accreditation
Q-2: What is needed to support community use of analytic tools?
A-1: A distributed collaborative framework
• Tools expressed as un-encumbered capabilities
• University certified educational support on all tools
A-2: Tool stability and tool interoperability
• Separation of all module services from vendor control
• Open-results competitive testing of all modules
A-3: Community based compensation infrastructure
• Commercial rights are protected with copyright and patents
• Use-compensation based on software self-accounting to honor
copyright and patents
• Micro-transaction accounting and payment for services embedded
in each software component.
Q-3: What are the benefits to Industry
A-1: Establish coherence within the market space
A-2: Advance the state of the art for information generation
systems and open new markets
A-3: Establish a new basis for innovation
A-4: Intellectual Property mapping and patent evaluation
will result in a reduction of uncertainty over ownership
Q-4: What are the Foundation Elements
A-1: Processes
• Text Transformed into Structured Data
• Unsupervised Pattern Mining
• Supervised Categorization
• Situational Logic Development
• Logical Inference
• Procedure Learning
• Event Detection from Data Invariance
• Knowledge Flow Mapping
• Social network and linguistic variation analysis
A-2: Subsystems
• Single-algorithm Analytic Servers
• Multiple User Domain
• Ontology based Inference Engine
A-3: The Human Element
• Knowledge Encoding and Propagation
• Information Visualization
• Cognitive Priming
• Multi-modal interaction
A-4: Single-Algorithm Analytic Servers
• Latent Semantic Technology
• Self-Organizing Maps
• Concept-Based Document Indexing
• Context-Free Grammar Parsing
• Clustering
• Supervised Text Classification
• Evolutionary Optimization
• Associative memory and top down expectation using neural
networks
• Social network theory and analysis
Q-5: Examples of Innovation
A-1: Categorical Abstraction
• Invariance in the data is used to construct situational logic
• Continuum mathematics methods are used to derive an "implicit
ontology" from a body of documents or other data sources
• An "explicit ontology" is provided by human beings,
e.g. in the form of categorized sentences, and then refined using
iteration
• Human feedback and inference rules are used to further refine
& process the derived classifications
A-2: Event Chemistry
• A technique for searching datasets for signs of real world
events
• Takes abstract atoms of invariance observed in data, and
forms interesting combinations of them
• Requires a Human-in-the-loop cognitive acuity to provide
interpretation of meaning
• Works naturally with the output of semi-supervised text classification,
clustering and categorization methodology
• Fits naturally with "chemical compound" metaphor,
where a period table of atomic elements are discovered and used in
event detection
A-3: Referential Bases
• Post relational database technology, using new types of algorithms
• (type:value) pair data constructions encode localization
of information without schema
• (type:value) pair data construction organizational processes
has well delineated correspondence to human memory and anticipation
• Referential bases support stratified processing so the ontology
constructions can be formative and situational
Q-6: Why are educational processes important?
A-1: The systemic development of educational processes involves
• the development of consensus on what are the separated techniques
in computational intelligence
• The mapping of scholarly literature helps in comprehensive
mapping of patent disclosure and copyright
A-2: As this consensus develops,
• the description of general systems theory, cognitive and
social science is made available within the academic community
• a "liberal arts" education in the knowledge sciences
is made available to intelligence analysts
Q-7: How does the software compensation model work?
A-1: Analytic features are to be replicated from existing
software and implemented as separated components.
• A mapping of all software based innovation in the area of
computational intelligence is developed based on latent semantic technology
indexing of patents and copyrights
• In cases where the core technology has legitimate ownership,
then licenses are arranged
• In cases where the core technology is developed by the government
then the core engines are made public domain
• Each core technology component is rendered in binary with
an internal accounting module that reports usage as part of a knowledge
flow mapping and use compensation (when appropriate)
Q-8: How are test sets made available to the competitive communities?
A-1: The system of core objects is open to innovation.
• Negotiations to acquire a new innovation occur through Intellectual
Property mapping processes and comprehensive testing of object inherit
capability
• Innovations targeted for acquisitions are studied in highly
structured usability testing that includes deep education in the innovations'
inherit capabilities.
• These acquisition studies are conducted in the public view
and are not governed by commercial processes.
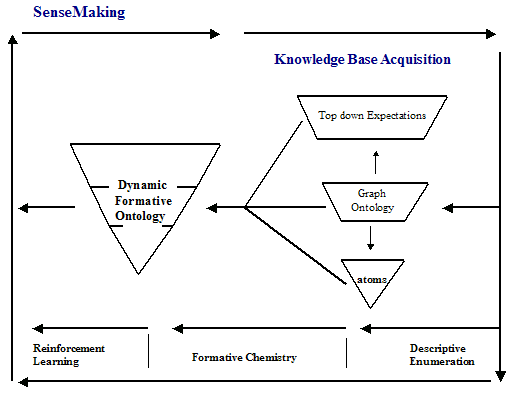
Knowledge Sharing and SenseMaking diagram
Contact:
Dr. Paul S. Prueitt
Research Professor
The George Washington University
Ontology Stream Inc
BCNGroup.org
703-981-2676

